 So what is the FODMAP diet? If you are one of the many people that struggle with gut health or mood swings based on your eating habits, this diet is a life saver. This diet was coined by Australian researchers that realized their patients suffering from Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) experienced a significant amount of relief when applying these restrictions to their current diet. This diet has shown great success in reducing constipation, bloating, gas, and abdominal pain, and will most likely help your digestive issues whether you have IBS or not. Check with your AZ family physician to see if these FODMAPs are the source of your digestive health issues.
So what is the FODMAP diet? If you are one of the many people that struggle with gut health or mood swings based on your eating habits, this diet is a life saver. This diet was coined by Australian researchers that realized their patients suffering from Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) experienced a significant amount of relief when applying these restrictions to their current diet. This diet has shown great success in reducing constipation, bloating, gas, and abdominal pain, and will most likely help your digestive issues whether you have IBS or not. Check with your AZ family physician to see if these FODMAPs are the source of your digestive health issues.
What Are FODMAPs?
According to the FODMAP Friendly Program, FODMAPs can be described as “short chain carbohydrates and sugar alcohols found in foods naturally or as food additives”. It’s scientifically proven that these carbohydrates and sugar alcohols trigger gut health problems because they are difficult for the small intestine to absorb. FODMAPs are fermented by bacteria in the large bowel, and also attract water which causes the bowels to move at a different pace than usual. The acronym FODMAPs can be specifically broken down to describe the carbohydrates and sugar alcohols as such: Fermentable:- Carbohydrates that are broken down by bacteria in the large bowel, as previously explained.
- Molecules made up of individual sugars joined together in a chain that is naturally digestion-resistant and moves through the intestines quickly.
- Found in fructans and galactooligosaccharides
- Commonly found in wheat, rye, onions, shallots, garlic, legumes, lentils, and artichokes.
- A double sugar molecule takes longer for the body to break down into monosaccharides.
- Found in lactose.
- Examples include milk, evaporated milk, custard, yogurt, and ice cream products.
- A single sugar molecule that is easily digestible but can cause stomach problems if consumed in excess.
- Found in fructose (in combination with the excess of glucose).
- Sugars found in honey, high fructose corn syrup, watermelon, mango, pears, and apples.
- Sugar alcohols used to replace sugar in certain foods, naturally or manually, and when consumed in a large amount can act as a laxative for the digestive system.
- Polyols are found in Sorbitol, Mannitol, Maltitol, Xylitol.
- Examples of polyols can be found in apples, pears, plums, nectarines, apricots, cauliflower, and any other products sweetened with polyols like gum or confectionery sugars.

How to Use the FODMAP Diet Properly
When you break down how much food contains FODMAPs, the idea of following a diet based on those restrictions may seem impossible. However, it’s not recommended to cut everything off at once, which is why the “FODMAP elimination diet” exists. The FODMAP elimination diet helps you find out which of the FODMAPs affects your body the most so that you don’t have to remove everything from your diet. You may start by eliminating one of the FODMAPs at a time, avoiding them for a month or two, and recording the results of your gut health along the way. Another method is to remove all FODMAPs from your diet and then slowly reintroduce them one by one to see which one affects your digestive system the most. Fortunately, even if you find that your stomach reacts poorly to lactose or glucose, you don’t have to give up every product that contains it. By consuming them in moderation, smaller portions, or just less than you usually would, you can avoid irritable bowel symptoms.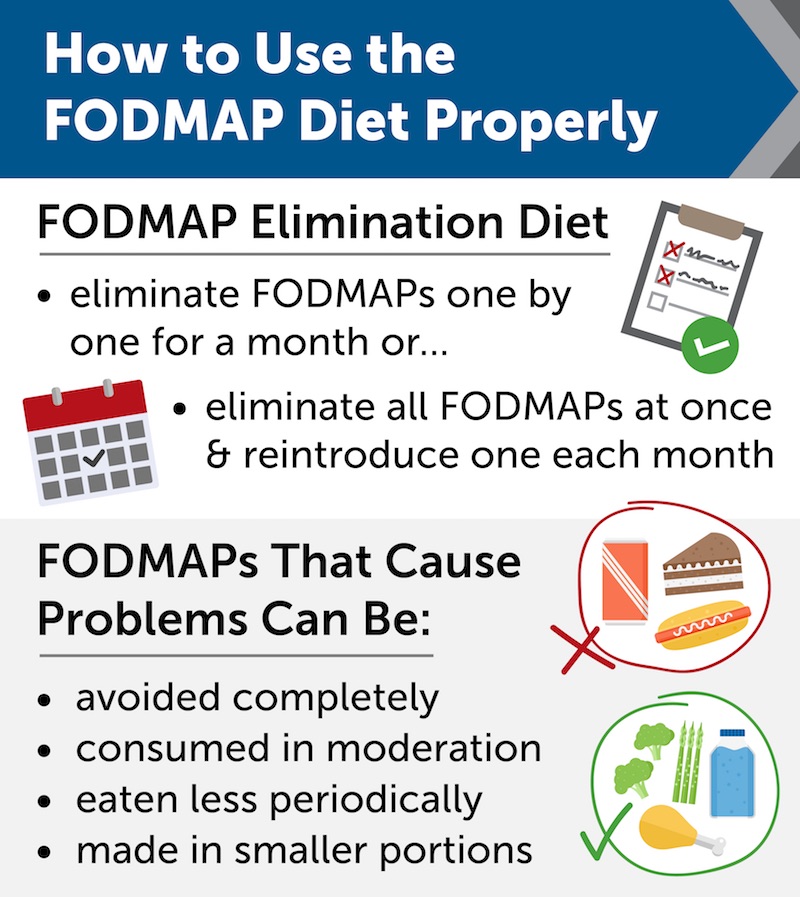
Diet-Related Illnesses
Practicing good nutrition is not only good for your gut health but can also save you from the many illnesses or diseases associated with a bad diet. Unhealthy eating can increase the risk of several diseases, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, osteoporosis, irritable bowel syndrome, and multiple types of cancer. Your mental health is also at stake when you are not treating your body right, which is why a person’s diet is often linked with their lethargy, depression, anxiety, and stress. To keep in the best mental and physical state possible, consider changing up what you eat, how often you eat, and the portions that you eat.
The Importance of Taking Care of Your Body
The food that you feed your body with is important fuel that not only affects your physical performance but your energy and mood as well. Whether or not you decide to implement certain aspects of FODMAP into your diet plan, you should always be wary of what you are putting into your body. The average person may not realize how damaging the type of sugars, fats, or carbs are in the food they consume every day. This is partially why nearly 29 million people in the U.S. are diabetic and one-third of the U.S. adult population is considered obese. Speaking with your family physician is the best way to find a course of action that meets your specific dietary needs. Arrowhead Health Centers is proud to offer programs for diabetes treatment and management to help their patients live a healthy lifestyle. To prevent future gut health problems, learn what diet suits your body best with an educated physician from Arrowhead Health Centers.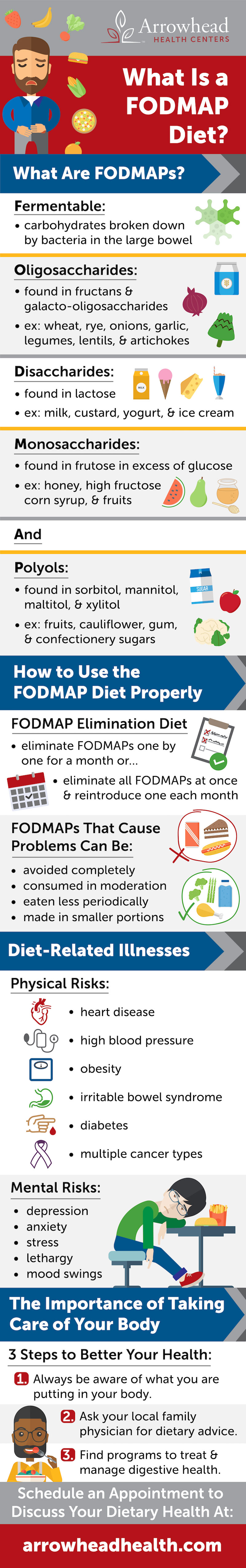




Leave a Reply